Non Terrestrial Network (NTN) overview
An exploration of the factors contributing to the rising popularity of NTN in the last years, its diverse applications, key challenges, strengths, and the promising future developments.
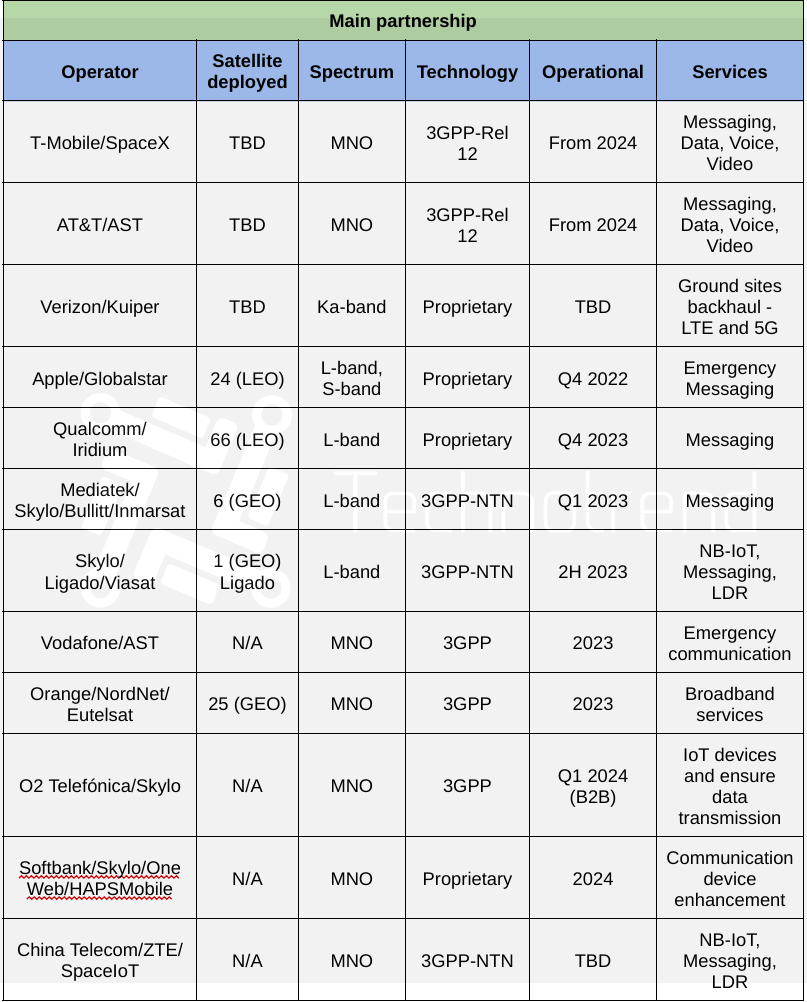
Above the main supplier scheme of Non Terrestrial Network industry
The reduction in the cost of NTN solutions, moves forward into a feasible and cost-effective option for ensuring communication everywhere. 5G standards advancements, satellite constellations, and 3GPP key players have performed a crucial role in driving technological progress in NTN systems.
One notable contributor to this surge is SpaceX's Starlink, showcasing NTN technologies that leverage space-based components to overcome the limitations of traditional networks. The critical mass reached by extensive satellite constellations, exemplified by Starlink, has established essential infrastructure for NTN services, likely aided by resolved regulatory approvals and heightened market demand.
Main Applications of NTN and comparison with GNSS positioning
NTN's applications span a multitude of industries, offering reliable connectivity in scenarios where traditional networks fall short. From emergency communication networks to efficiently offloading traffic during peak times, NTN has found its place in diverse sectors. Hybrid cellular/NTN-connected devices prove particularly beneficial for activities like extreme sports, ensuring a reliable connection in areas with intermittent cellular coverage.
Industries such as automotive, energy infrastructure, agriculture, maritime, and railway sectors now have access to seamless global communication, even in the most remote locations. Remote installations like maritime shipments, offshore oil rigs, and trains, beyond the reach of cellular networks, find NTN as a reliable option for monitoring and controlling operations.
NTN, particularly in the context of Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) asset tracking, agriculture, and equipment monitoring, offer distinct functionalities compared to Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS).
1. RTLS Asset Tracking:
- NTN Technology: NTN technologies in RTLS asset tracking utilize a combination of satellite-based or airborne platforms to provide real-time location information. The use of satellites or high-altitude platforms enhances coverage, making it suitable for tracking assets globally. NTN can offer precise location data with low latency, enabling accurate tracking of assets in various environments.
- Comparison with GNSS: While both NTN and GNSS aim to provide location information, NTN can be advantageous in scenarios where GNSS signals may be obstructed, such as in dense urban environments or indoors. NTN offers an alternative or complementary solution for asset tracking, ensuring more comprehensive coverage.
2. Agriculture:
- NTN Technology: In agriculture, NTN technologies can play a crucial role in providing connectivity to remote rural areas. Farmers can leverage 5G NTN for applications like running unmanned tractors, monitoring livestock, and obtaining real-time data on crops. The high bandwidth and global coverage make NTN beneficial for precision agriculture and smart farming.
- Comparison with GNSS: GNSS, including systems like GPS, is fundamental for location-based services in agriculture. It provides accurate positioning information for tasks such as precision planting and harvesting. NTN complements GNSS by offering additional connectivity for data transfer and communication in areas where traditional terrestrial networks might be limited.
3. Equipment Monitoring:
- NTN Technology: NTN technologies facilitate continuous monitoring of equipment in remote locations, such as oil rigs. Sensors and trackers, along with NTN connectivity, enable real-time data transmission, ensuring efficient equipment management. This is particularly valuable for industries where timely monitoring and maintenance are critical.
- Comparison with GNSS: GNSS contributes to equipment monitoring by providing location data, helping track the movement of assets. However, NTN goes beyond by offering a communication infrastructure that supports constant monitoring, data transmission, and control of equipment in real-time. It enhances the overall efficiency of equipment management.
In summary, NTN technologies bring a global and connected dimension to RTLS asset tracking, agriculture, and equipment monitoring. While GNSS remains fundamental for location-based information, NTN complements and extends these functionalities by providing reliable, high-bandwidth communication in diverse and remote environments. The combination of both technologies can create a comprehensive solution for various applications.
Main Challenges and Strengths of 5G NTN
While NTN solutions hold a great potential, on the other hand there are also challenges. Higher latencies, doppler shifts, and handover complexities pose potential barriers for 5G NTN operations. Yet, ongoing efforts by 3GPP, addressing compatibility challenges within 5G standards, suggest a commitment to overcoming these obstacles.
The strength of NTN lies in its ability to provide connectivity in challenging-to-access areas, offering a reliable solution for emergencies and seamless global communication. The integration of NTN into 5G standards enhances interoperability, making it more appealing to network operators, and economic viability has been achieved through reduced satellite launch costs and infrastructure advancements.
Future Developments and Conclusion
The future of NTN holds promise, with ongoing technological advancements and a growing interest in private space companies. Efforts to reduce orbital launch costs and innovations in low-power radio and advanced modulation schemes aim to enhance the efficiency and reliability of NTN connections.
As 3GPP standards continue to drive innovation and integration with terrestrial networks, NTN is poised to become a ubiquitous part of global connectivity. The prospect of 'mega-constellations' and a decline in associated costs suggest broader accessibility to NTN solutions across businesses of varying sizes for their IoT applications.
In conclusion, 2023 marks a pivotal moment for NTN technologies, transforming global connectivity through seamless integration of space-based components. With collaborative efforts to overcome challenges, the future promises a world where NTN leads the way in shaping telecommunications and space exploration, offering a connected future for businesses and individuals.